Step 1. Alignment and peak picking
 After importing the tutorial archive, the experiment opens at the Import Data
screen (shown here at the right). Progenesis LC‑MS immediately begins to load the LC‑MS runs that it contains. During this, the runs are
also examined to find any problems that might affect the reliability of your analysis. The imported runs are
listed at the left of the screen, with the selected run's ion intensity map shown at the right.
After importing the tutorial archive, the experiment opens at the Import Data
screen (shown here at the right). Progenesis LC‑MS immediately begins to load the LC‑MS runs that it contains. During this, the runs are
also examined to find any problems that might affect the reliability of your analysis. The imported runs are
listed at the left of the screen, with the selected run's ion intensity map shown at the right.
For this tutorial experiment, none of the runs has a problem that might affect analysis, so we can move on to the next stage of analysis. Click the Section Complete button at the bottom-right of the screen.
Selecting a reference run
Before we can begin aligning our runs—a process that is critical to the analysis—we must choose one run that is the most representative of our data. All other runs will then be aligned to this before we detect the peptides' locations in the ion map.
For this tutorial, the representative run is A1. Select it in the list and click the Use as reference run button. We can now begin aligning our runs; click Section Complete to continue to the Alignment screen.
 Aligning the runs
Aligning the runs
Alignment of the LC‑MS runs is required in the LC (retention time) direction. It is key to correcting for the variable elution of peptides during chromatographic separation and can be performed either manually, automatically, or by a combination of the two approaches.
For this tutorial, we'll use fully automatic alignment. It is a good idea to use this approach whenever possible, because it enhances the reproducibility of your analysis.
Click the Automatic Alignment button to align the runs to the reference. When asked which runs you want to align, leave all of the runs selected and click the OK button. The software will then begin the alignment process, which may take a few minutes.
When the automatic alignment finishes, click Section Complete. The Peak Picking Parameters window will appear, giving us the chance to fine-tune the peak picking (i.e. the process by which we find the peptides in our samples). For the tutorial, leave all parameters as they are and click the Start peak picking button. The software will then spend a few minutes finding the peptides in the runs.
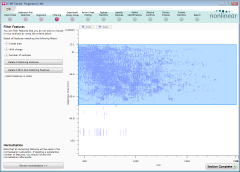 Removing unreliable features after peak picking
Removing unreliable features after peak picking
When peak picking finishes, the Filtering screen shows the location of the peptide ions we found; each is referred to as a feature.
We can now remove any features whose analysis we believe may not be reliable. This is done by specifying various properties—retention time, charge, and so on—that must be matched.
First, we'll remove features with early or late retention times:
- On the image, drag out an area like that shown above (click the image for more detail). To ensure we include all peptides with a low mass/charge value (those at the left side of the screen), start the drag near the top-right and drag to the bottom-left of the main elution period.
- Click the Delete Non-Matching Features button to remove the features not inside this area.
Next, we'll restrict our analysis to peptides with a charge in the range 2 to 7 inclusive:
- Start by clicking on the Inside area option to close it.
- Click on the With charge option to expand it.
- Select Charge 2, Charge 3, Charge 4 and so on, up to and including Charge 7.
- Click on the Delete Non-Matching Features button.
This leaves us with all of the features that have a charge state between 2 and 7, and none of the features that eluted either very early or very late. We are now ready to identify the features whose behaviour varies across the runs. Click Section Complete to continue…





